DataWeb FAQs
Account Setup
DataWeb relies on Login.gov to authenticate users in the application. If you have not already created a Login.gov account, you can do so here: Create an account | Login.gov
This could be for several reasons, such as:
- You don’t have a login.gov account. Click here to create one.
- You haven’t properly authenticated with Login.gov.
- Your browser may be caching old data that is no longer valid.
- Your I.T. Department could be blocking your access to some applications.
- Your browser might have an old version of the application. Please see "How do I clear my browser's cache"
Querying and Downloading Data
Product classification begins with finding the correct classification for your product in the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTS or HTSUS) maintained by the USITC. The HTS is accessible at https://hts.usitc.gov/. If you are new to using the HTS or want a refresher, the USITC developed this online tutorial to assist users in understanding how to use the HTS that you may find helpful: https://learning.usitc.gov/hts-guide/index.html. The HTS is maintained by the Office of Tariff Affairs and Trade Agreements https://www.usitc.gov/offices/tata.
You can only create saved groups after logging into a DataWeb account.
In Step 3: Countries, Step 4: Commodities, or Step 7: Districts, click the How would you like to choose… field and click Select Individual…
- A Select Individual… field appears. Select all the countries/commodities/districts to add to your custom group.
- If you have also manually entered country or commodity codes, click Add after each entry.
- Click Save Group
- A popup appears. Enter a group name and click Save … Group.
- The How would you like to choose… field now defaults to the Select … Groups.
Note: In the steps above, “…” is used to represent Countries, Commodities, or Districts.
In Step 4 on the New Data Request page, click on Select Individual Commodities in the top entry box. Enter or search for commodity codes or make selections from the provided list of commodities. Once all the commodities of interest have been entered or selected, choose the aggregation for the commodities, and then continue with any other steps in the data request.
When querying, you can select Download Data at the bottom of the page. Alternatively, click Download Data at the top of the results page of any data request. You can also select Download Data from the Saved Query page.
To use the Commission's DataWeb system to get U.S. trade data, go to: https://dataweb.usitc.gov/. Most queries can be performed without logging in. To save queries, share queries, or use the API, you must have an account. Loging into DataWeb requires multifactor authentication and DataWeb uses Login.gov for this purpose. The instructions to link your Login.gov account can be found at https://www.usitc.gov/dataweb_login_process.
On the first page, select the type of trade you are interested in reporting under the "TRADE" heading. You can select domestic exports, foreign exports or re-exports, total exports, U.S. imports for consumption, general imports, or trade balance.
On the following page, make all selections you desire. In “STEP 1” you can change the Trade Flow or Classification System (e.g., HTS, NAICS). You can select the data measure and timeframe under the "STEP 2" heading. Under the "STEP 3" heading you can select data from all countries, select individual countries from a list, or select country groups. You can select all commodities, individual commodities, or commodity groups under the "STEP 4" heading. When you select individual commodities, you can scroll though the list of options and select the desired code or type the HTS code or NAICs code in the text box. If you are querying imports for consumption “STEP 5” allows you to choose specific import programs and “STEP 6” allows you to select different rate provision codes. “STEP 7” allows you to select different districts of entry or export. “STEP 8” and “STEP 9” provide you with the ability to change the sorting and formatting of the data output. “STEP 10” allows you to convert the units of quantity to another unit (e.g., kg to mt) if you selected First or Second Unit of Quantity in “STEP 2”. If you have logged in to an account, “STEP 11” provides the ability to save the query and has an option to send the query results in a monthly report to the email associated with your account (which is typically useful if you choose something other than “Annual” in “STEP 2: Timeframe Aggregation”.
Once you have made all your selections, select the "Download Data" or “View Results” button at the bottom of the page. The downloaded data will be in an Excel format, and the view results option provides the data in your web browser.
The web browser interface can only render 10,000 rows or less. When downloading data into Excel, the data can include significantly more rows, but it is not unlimited. Downloaded data may be limited to 300,000 of fewer rows. Sometimes depending on system use that limit can be higher but the limit will never exceed Excel’s row limitations. For larger data pulls, users can use the API. To use the API, the users must have an account. Refer to the API documentation for more information on how to use this tool.
There is an API. To use the USITC API, you must have an account. Refer to the API documentation for more information on how to use this tool.
Currently, the USITC does not maintain data in electronic format that goes back further than 1989. The U.S. Census Bureau has a Statistical Abstract Series that dates back to the 1870s, but you will have to read through the documents to search for the information you are looking for.
https://www.census.gov/library/publications/time-series/statistical_abstracts.html
SITC data can be queried. When creating a query, users can select different classification systems in Step 1. The options are HTS Items, SIC codes, SITC codes, and NAICS codes. Users do not have the ability to query end-use data in DataWeb.
Monthly Data Releases and Data Updates
Monthly data is released in DataWeb about three business days after the Census Bureau releases the data. Census’s release schedule can be found here: https://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/schedule.html.
If you have created an account, you can request to receive an email notification when the data is updated. To find this option, go to the Trade Dashboard, which is under the Trade heading on DataWeb’s main page (https://dataweb.usitc.gov/). This option only appears when you are logged in. There is a tab in the Trade Dashboard page called Notifications. You can select a toggle to receive email notifications within the Notifications tab.
The Census Bureau revises historical data each June for the three immediately preceding calendar years. For example, in June 2024, Census published revisions impacting trade statistics impacting data for 2021, 2022, and 2023 calendar years. The USITC’s DataWeb incorporates these Census Bureau revisions shortly after their publication, but because they are revising thirty-six months of data it typically takes the USITC slightly more time to update the database than with the normal monthly releases.
The data subject to these annual Census Bureau revisions are separately posted by the Census Bureau in a running spreadsheet format on its corrections page. Users wishing to know whether any specific country or HTS number may be impacted by a future Census Bureau revision release may check this website: https://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/statistics/corrections/index.html. If an error is discovered more than three years in the past, the correction will not be reflected in the official US trade data or in DataWeb.
DataWeb only contains the public official U.S. merchandise trade statistics published by the U.S. Census Bureau in which individual company-level details are aggregated in such a way to not disclose confidential (firm-level) information. The firm-level data used to construct these statistics are maintained by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) agency of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. If you wish to gain access to more detailed, company-level data you would have to submit your inquiry to CBP: https://www.cbp.gov/contact.
Definitions and Classifications
The first unit of quantity refers to the first (if any) statistical reporting unit specified in the HTSUS (for imports) or Schedule B (for exports) applicable to the specific product classification selected. Note that not all product classification codes (10-digit HTS statistical reporting numbers for imports, or 10-digit schedule B numbers for exports) require importers or exporters to report a quantity measure.
The second unit of quantity refers to the second (if any) statistical reporting unit specified in the HTSUS or Schedule B applicable to the specific product classification selected. Note that most product classification codes do not require importers or exporters to report a second quantity measure.
Information as to whether importers must report a “first unit of quantity” and/or a “second unit of quantity” for any given product being imported is maintained in the HTSUS. In the example below all 10-digit statistical reporting numbers listed have a first unit of quantity of “No”, which represents number or units, and certain 10-digit statistical reporting numbers listed below (for example 8541.42.0010 is the first) also have a second unit of quantity of “W”, which represents watts. When the HTSUS show one or two “unit of quantity” next to a statistical reporting number, importers are required to submit data on those aggregated quantities (in addition to value) for its imports within their entry summary paperwork.

On the query design page, there are blue question marks that open dialogue boxes with definitions. On Step 1, there is a question mark near “Trade Flow”. This question mark opens a dialogue box with definitions for the different trade flows such as domestic exports and imports for consumption.
On the query design page, there are blue question marks that open dialogue boxes with definitions. On Step 2, there is a question mark near “Data to Report: Summable Measure”. This question mark opens a dialogue box with definitions for the summable variables such as customs value and landed duty paid value. Definitions for the summable values and quantities can also be found on Census’ website at https://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/reference/definitions/index.html .
Schedule B is used to classify products for U.S. exports and is administered by the U.S. Census Bureau. You can search for schedule B numbers at https://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/schedules/b/index.html. For U.S. imports, the Harmonized Tariff System (HTS) is used, and it is administered by the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC). You can search for HTS numbers at https://hts.usitc.gov/.
Product classification begins with finding the correct classification for your product in the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTS or HTSUS) maintained by the USITC. The HTS is accessible at https://hts.usitc.gov/. If you are new to using the HTS or want a refresher, the USITC developed an online tutorial to assist users in understanding how to use the HTS that you may find helpful: https://learning.usitc.gov/hts-guide/index.html. The HTS is maintained by the Office of Tariff Affairs and Trade Agreements https://www.usitc.gov/offices/tata.
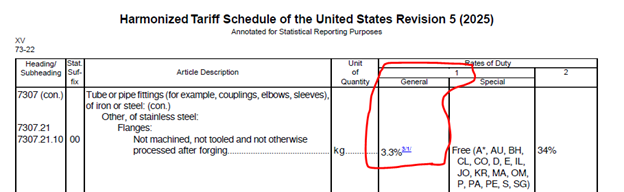
Duty rates are listed for most U.S. trading partners under the column 1 “General” (normal trade relations, previously referred to as most favored nation, rate), highlighted in red below. Some U.S. trading partners may have access to lower or eliminated duty rates based on trade preference programs (e.g., GSP, AGOA) or free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, Korea-US FTA), those are shown under column 1 “Special”. A handful of countries are not eligible for normal trade relations rates of duties (currently North Korea, Cuba, Russia, and Belarus) and imports from these countries would be subject to the column 2 rates of duty. Additional duties or import restraints (quotas) may also be applicable depending on the product / country of origin based on other statutory authorities (e.g., 232 aluminum and steel tariffs, 301 China specific duties), all of which are laid out in Chapter 99 of the HTSUS.
It should be noted, however, that the USITC is not authorized to provide legally binding interpretation on how to classify goods according to the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States and, thus, is unable to confirm to the public what the final duty rates for their imports will be. That authority resides with the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) agency of the Department of Homeland Security. Only CBP can issue legally binding rulings or advice on the tariff classification of imports. You can submit an inquiry to CBP at: https://www.cbp.gov/contact.
For import statistics, the countries in DataWeb are the “Country of origin,” as reported to CBP. The country of origin does not change for a product that is processed in a third country and/or shipped through a third country. The country of origin is a specific legal reporting requirement. The rules of origin requirements differ based on where the good was manufactured and on the product being reported. For example, paper that has been produced in Germany but cut to size in France could still be reported as country of origin Germany if that is what the country-of-origin reporting requirements are for that product.
For export statistics, the countries in DataWeb are the country of ultimate destination where the goods will be consumed, further processed or manufactured, known at the time of exportation by the shipper. For example, if an exporter is transporting goods from the United States via truck to Guatemala, the country in export statistics will be identified as Guatemala even though the trucker first entered Mexico, and even if the trucker leaves the goods in Mexico for another carrier to complete the shipment down to Guatemala.
The first six digits of Schedule B and HTS numbers are the same because the United States, as well most global training partners, are a member of the global harmonized system (HS) system of nomenclature promulgated by the World Customs Organization (WCO). However, at the 8 – and 10 – digit statistical reporting number, U.S. import and U.S. export classifications schemas differ. In fact, there are more 10-digit HTS statistical reporting numbers than there are 10-digit Schedule B statistical reporting numbers. Given there are more import numbers than export numbers, multiple HTS 10-digit statistical numbers often correspond to one or more Schedule B 10-digit statistical reporting number. HTS numbers are more detailed as they are used by Customs and Border Protection (“CBP”) to monitor and record U.S. imports as well as to apply duties. For more information, please visit https://www.census.gov/newsroom/blogs/global-reach/2018/07/exporting-with-import-class-numbers.html.
Other Data Related Questions
Some query parameters have changed or are no longer available from the previous version of DataWeb. This may cause some migrated queries to fail. If a query fails in the Saved Query page, you can select the query (from the Saved Query page), and after making the necessary updates, select Update Query to save the query with corrected parameters.
This is a marker the USITC created to indicate when there is likely suppression of quantity data by the Census Bureau in published official merchandise trade statistics. The data released by Census does not contain information or any indication of data suppression. However, the USITC can identify certain line items in the Census datafiles where, based on the HTS or Schedule B, a line should have reported a quantity. If the quantity data are missing from that field, DataWeb has flagged that record as potentially having suppressed quantity data. When applicable, these data flags are identified with stars in the various quantity aggregations conducted by users in the application to alert the users their aggregation contains one or more records with likely suppressed quantity data. The discovery that there were suppressed quantity data in the Census Bureau data files is also the reason for which we have disabled the application’s calculation of average unit values (AUVs) since such calculations can be significantly distorted depending on the amount of quantity data that has been suppressed within a specific query.
The suppressed columns indicate one or more entries included in the aggregate did not have its first unit of quantity data reported. This could be because it was redacted by Census in the publication of official import statistics or the importers in question failed to provide data for the first unit of quantity. Only aggregations where a first unit of quantity was required according to the HTSUS (for imports) or Schedule B (for exports) are flagged.
Official U.S. import statistics do not include transshipments, neither for imports for consumption nor for general imports. Physical arrivals into ocean ports or airports that then get shipped to another country are not included in official statistics. Likewise, imports that have been cleared with the legal requirement of being re-exported such as under the temporary in bond (TIB) program are generally excluded from official import statistics.
Unfortunately, bill of landing (BOL) data is not available in official U.S. import statistics. While bills of lading and other shipment information along with Form 3461 (Customs Release) are required to be filed for goods to be entered into the country, these submissions are not the basis for import statistics because they do not contain the necessary data granularity needed for the creation of official U.S. import statistics. The Census Bureau instead uses data submitted to CBP by the importers of record in their entry summary paperwork, Form 7501 (which is submitted later in the import process typically after the cargo has already been released by Customs). As a result, any cargo release information, including the bills of lading, are not available on DataWeb. You will need to contact U.S. Department of Homeland Security, Customs and Border Protection (CBP) to get more detailed data from the cargo release process.
Imports of textile and apparel goods benefitting from trade preferences under the Haiti HOPE, HOPE II, or HELP Acts are not flagged as a special import program in official U.S. import statistics. The Haiti HOPE marker in DataWeb was generated by the USITC. Imports for consumption that meet three criteria were marked with this program marker: 1) country of origin is Haiti, 2) no other program was indicated (00-No program claimed) in the special import program field, and 3) a rate provision code of 18, which indicates the product was imported under a duty-free special import program.
Unfortunately, the data contained in DataWeb does not contain state level data. However, the US Census does report some trade data at the state level. For more information, please visit https://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/statistics/historical/state.html
Other
The commodity translation tool allows users to translate individual numbers using a known HTS, SITC, or NAICS number.
When using these data, the USITC suggests that the following citations be used:
Citations to merchandise trade data (imports/ exports):
Source: Compiled using the U.S. International Trade Commission’s DataWeb (https://dataweb.usitc.gov/) from official U.S. merchandise trade statistics published by the U.S. Department of Commerce, Census Bureau, accessed XXX.
Citations to tariff data:
Source: U.S. International Trade Commission’s Tariff Database, accessed via DataWeb (https://dataweb.usitc.gov/) on XXX. For official tariff information, however, please refer to the U.S. Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) available at https://hts.usitc.gov/.
You can contact the USITC using the form here: https://www.usitc.gov/applications/dataweb/dataweb_5_help